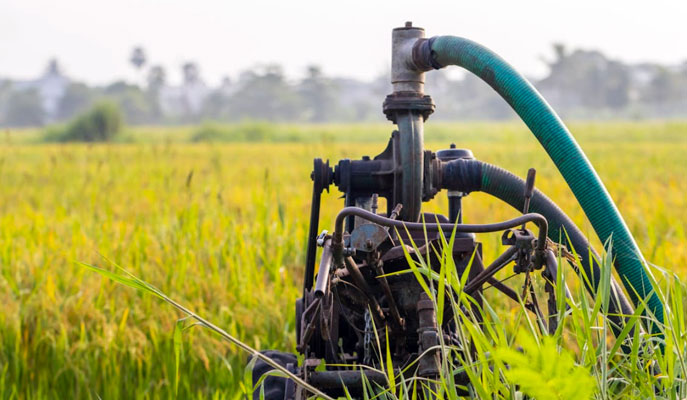
Water management is a critical aspect of agriculture, landscaping, and various industrial applications. With increasing demands for water resources, the efficiency and effectiveness of irrigation systems have never been more crucial. One essential component of these systems is irrigation pumps, which help distribute water to crops, gardens, and land optimally. These pumps save time and labor and promote a more sustainable approach to water usage. Understanding the operational mechanisms, types, and benefits of irrigation pumps can significantly enhance water management practices. They facilitate the transport of water from various sources, ensuring that every drop counts in promoting growth and preventing wastage in this resource-limited environment.
The Mechanisms of Irrigation Pumps
Irrigation pumps can be classified into several categories, each designed to meet specific water distribution needs. Broadly, the two main categories of pumps are positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps. Positive displacement pumps operate by moving fluid into a chamber and then forcing it out, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. On the other hand, centrifugal pumps utilize a rotating impeller to force water outwards, creating a flow. This type of pump is generally favored in agricultural settings due to efficiency and speed.
Understanding the specific requirements of your irrigation system can help in determining the most suitable pump type. The efficiency of a pump is influenced by various factors, such as the pump’s size and the required head, and the height of the water that needs to be lifted. Selecting the correct pump size can significantly impact energy consumption and operational costs. An oversized pump may consume unnecessary energy, while an undersized pump may result in inadequate water delivery.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Pump
Identifying the correct irrigation pump hinges on a thorough understanding of your water source, land needs, and agricultural goals. Residential systems often require smaller, less powerful pumps, while agricultural or commercial setups may necessitate more robust models capable of covering large areas. Factors like water source—be it a well, river, or lake—play a crucial role in pump selection, as some pumps are better equipped to handle specific conditions. To effectively pump your lake water can serve a vast array of irrigation needs, maximizing the potential of existing natural resources. Considering the pump’s power source is equally important.
Electric pumps generally offer reliability and efficiency, while diesel or gasoline pumps are advantageous in remote areas where electricity may not be accessible. Striking a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness will yield the best results for any irrigation system. You can further enhance water management by incorporating features like variable speed drives, which allow for better control over water flow depending on weather conditions or plant growth stages.
Benefits of Using Irrigation Pumps
Integrating irrigation pumps into water management practices results in several noteworthy benefits. The most apparent advantage is the enhancement of water efficiency. Efficient pumps minimize the chances of over-irrigation and reduce runoff, ensuring that water is utilized directly where needed. This effective allocation helps conserve water, particularly crucial in arid regions where resources are scarce.
Using pumps allows water to be delivered at optimal times, avoiding evaporation losses that are common during peak sunlight hours. Another significant benefit is improved soil health and crop yields. Proper water supply ensures that crops receive adequate moisture, contributing to better plant health and higher productivity. Consistency in irrigation reduces plant stress and maintains even moisture levels in the soil, which is critical for germination and growth.
Challenges Associated with Irrigation Pumps
Despite their advantages, there are challenges related to the use of irrigation pumps. System maintenance is one such issue that cannot be overlooked. Regular upkeep is essential, as pumps can become clogged with debris, affecting their operational efficiency. Neglecting maintenance tasks can lead to pump failures, resulting in crop loss and increased costs.
Understanding the complexities of pump systems may pose a challenge for less experienced users. Training and education on system management can bridge this gap, allowing users to maximize the benefits of their irrigation pumps. Cost is another pivotal concern. The initial investment in purchasing and installing a good-quality pump can be significant. Ongoing utility costs can burden budgets, primarily if the system operates inefficiently.
Innovative Technologies in Irrigation Pumps
The evolution of technology continues to reshape the landscape of irrigation pumps. Advances in smart irrigation technology, including sensors and automated controls, facilitate real-time monitoring and management of water distribution. These innovations enable farmers and landowners to adjust irrigation schedules based on weather patterns, soil moisture levels, and plant needs with more precision. Adopting smart technology saves water and enhances crop production while protecting the environment.
Mobile applications that monitor pump performance and adjust operations in real-time are gaining popularity. Such tools empower users with data-driven insights, leading to more strategic decision-making. Innovations extend to the design of pumps themselves, with many manufacturers now creating more efficient, durable pumps that can withstand the rigors of outdoor environments. As these technologies emerge and improve, their role in sustainable water management becomes ever more significant.
Environmental Impact of Irrigation Pumps
While the focus often lies on efficiency and performance, the environmental impact of irrigation pumps should be considered. Excessive water extraction can lead to depletion of natural water sources, affecting local ecosystems. This emphasizes the need for sustainable water management practices that balance irrigation needs with conservation efforts. Every action taken to optimize irrigation can make a notable difference, and proper planning can mitigate harmful effects on the environment.
Monitoring the energy consumption of irrigation pumps is essential. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power can offset the carbon footprint associated with traditional fuels. As the world moves toward greener practices, adopting eco-friendly solutions in irrigation can contribute to broader environmental goals. Integrated water resource management combines economic, social, and environmental perspectives for a sustainable future.
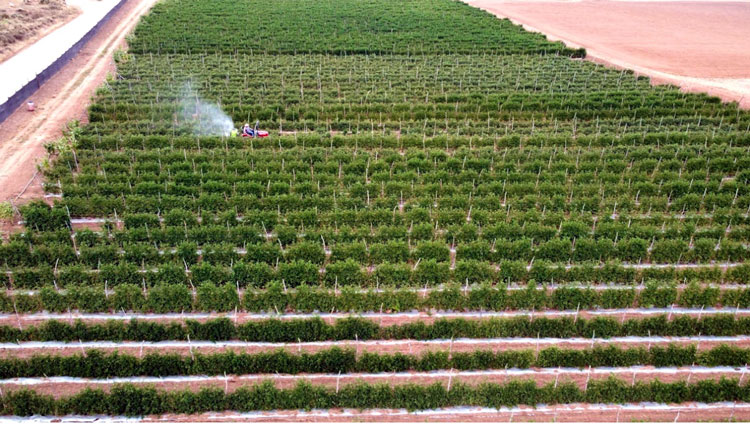

Striking a balance between modern innovations and traditional methodologies can yield optimal results. By fostering awareness and promoting sustainable systems, irrigation pumps can continue to serve as vital components in water management, ensuring food security and preserving water resources for future generations.